As the legal use of weed and other marijuana products grows, consumers are becoming conscious of their options, and the different chemicals extracted from cannabis. This includes the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), two of the many naturally active compounds found in cannabis. There are 85 cannabinoids that we know of in marijuana.
CBD is extracted primarily from the hemp plant and has no psychoactive compounds. The hemp plant is grown for products such as hemp seeds, nutritional supplements, hemp oil, and fibers for clothing and paper. Ingestible CBD is sold in gummies, oils, tinctures, extracts, isolates, supplements and more.
THC is the primarily psychoactive compound in marijuana that gives the user a “high” feeling. You can ingest it by smoking, which is the fastest way to feel the effects. It’s also available in edibles, oils, capsules, and tinctures, among others.
Each of the many cannabinoids from marijuana have different effects; this article focuses on the two most abundant, and well-researched, cannabinoids in marijuana.
1. Chemical Structure
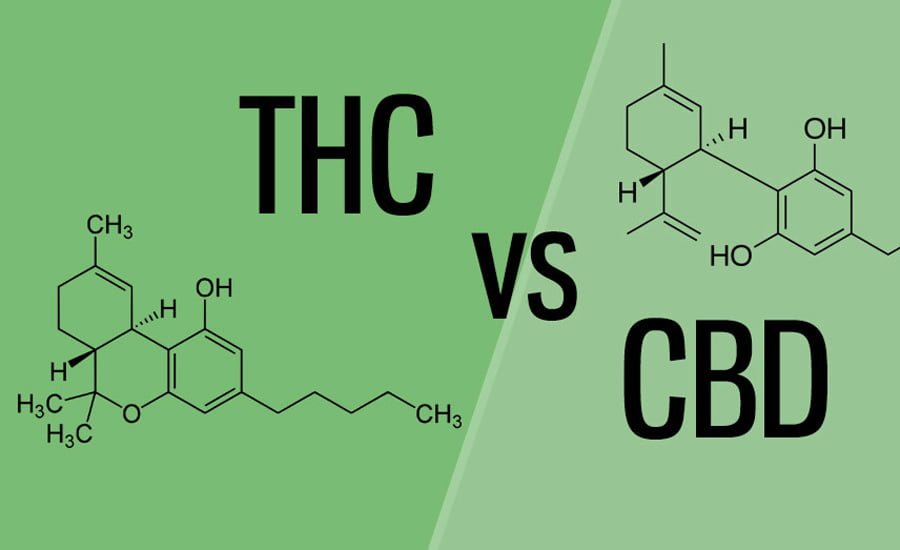
Both THC and CBD, being cannabinoids, have similar molecular structure. All have 21 carbon, 30 hydrogen, and 2 oxygen atoms. What differentiates THC from CBD is the arrangement of a single atom.
These compounds interact with the “endocannabinoid” system in your body, which is part of the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, and peripheral neurons and neurotransmitters). Endocannabinoid receptors and neurotransmitters are responsible for regulation of such things as mood, appetite, fertility, pain-sensation, memory, exercise-induced euphoria, metabolism, immune function, and regulation of cannabinoids from marijuana.
2. Psychoactive Components
Despite having a similar chemical structure, THC and CBD have very different effects because they activate different kinds of receptors in the nervous system. The main difference is that THC is psychoactive, whereas CBD is not.
CBD doesn’t give the high feelings associated with THC, because THC activates CB1 receptors in your brain to produce a feeling of euphoria. CBD, on the other hand, primarily activates CB2 receptors in your brain and peripheral nervous system. CBD can also bind with CB1 receptors in a way that prevents THC from activating the receptor, even when present at the CB1 receptor site. This means that CBD may partially neutralize the effects of THC – but more research needs to be done on this by medical professionals.
3. The Medical Benefits
THC and CBD have very similar medical effects. You can use them to seek relief for most medical conditions, such as anxiety, insomnia, appetite stimulation, mood regulation, and pain relief.
However, CBD doesn’t give the euphoric feeling common with THC compounds. Some people may choose to use the CBD compounds because of this feature. For example, it is illegal to drive with THC in your system but not illegal to drive with CBD. This can make CBD oil a better choice for chronic conditions like pain and anxiety.
In June last year, the US FDA approved the use of CBD to treat a rare type of epilepsy. Other than this, CBD is also used to treat conditions like:
- Inflammation
- Seizures
- Psychosis
- Nausea
- Migraines
- Anxiety
- Depression
THC can be helpful in these conditions:
- Muscle spasticity
- Glaucoma
- Nausea
- Low appetite
- Anxiety
4. Side Effects
Most people are highly tolerant to CBD, even in extremely large doses. According to various research, the side effects associated with CBD are due to interactions with another form of medication you’re taking.
On the other hand, THC has lots of side effects due to its psychoactive features. These include:
- Coordination problems
- Dry mouth
- Increased heart rate
- Slow reaction time
- Red eyes
- Memory loss (particularly with chronic use)
Neither of these compounds is fatal, in large doses or over long stretches of time. However, chronic long-term THC use may result in negative psychiatric effects including loss of memory and poor motor coordination. The negative effects are worse when THC use begins in adolescence.
Conclusion
THC and CBD, both legal in Canada, have similar molecular structures, but very different effects on the body. CBD, usually extracted from hemp plants, can be a great choice for individuals looking for the medicinal benefits of marijuana, without the psychoactive “high” associated with THC.








Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.